Amazon_Vine_Analysis
Overview
We were tasked with the following project: analyzing Amazon reviews written by members of the paid Amazon Vine program. The Amazon Vine program is a service that allows manufacturers and publishers to receive reviews for their products. Companies like SellBy pay a small fee to Amazon and provide products to Amazon Vine members, who are then required to publish a review.
In this project, we had access to approximately 50 datasets. Each one contains reviews of a specific product, from clothing apparel to wireless products. We needed to pick one of these datasets and use PySpark to perform the ETL process to extract the dataset, transform the data, connect to an AWS RDS instance, and load the transformed data into pgAdmin. Next, we used PySpark (could alternatvely have used either Pandas or SQL) to determine if there is any bias toward favorable reviews from Vine members in your dataset. Then, we wrote this summary of the analysis for the stakeholders.
Technologies Used:
- Amazon Reviews Data (https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazon-reviews-pds/tsv/index.txt)
- PySpark
- Google Colab
- Amazon AWS
- S3
- RDS with PostgreSQL
- pgAdmin
A detailed summary of the Amazon Review datasets for all categories is shown in Appendix A.
Results
Deliverable 1 - Perform ETL on Amazon Product Reviews
Using our knowledge of the cloud ETL process, we created an AWS RDS database with tables in pgAdmin, picked a dataset from the Amazon Review datasets (Links to an external site.), and extracted the dataset into a DataFrame. We transformed the DataFrame into four separate DataFrames that match the table schema in pgAdmin. Then, we uploaded the transformed data into the appropriate tables and ran queries in pgAdmin to confirm that the data has been uploaded. For detailed listings and figures, please refer to Appendix B.
In addition, runtimes were recorded for both Deliverable 1 and Delverable 2 in Table 1 below. The runtimes were dramatically different on an early Saturday morning (fast) vs. Weekdays (very slow).
Table 1 - Runtimes for two sample datasets
| Step | Books | Furniture |
|---|---|---|
| Download Review Data from Amazon | ~5m | ~1m |
| Write review_id_df to RDS | 12m 53s | 2m 10s |
| Write products_df to RDS | 3m 29s | 1m 15s |
| Write customers_df to RDS | 4m 19s | 1m 44s |
| Write vine_df to RDS | 12m 42s | 2m 10s |
| Read review_id_table back to PySpark Notebook | ~1s | 46s |
| Read products_table back to PySpark Notebook | ~1s | 9s |
| Read customers_table back to PySpark Notebook | ~1s | 11s |
| Read vine_table back to PySpark Notebook | ~1s | 28s |
| Calculate bias statistics | ~36s | ~10s |
Deliverable 2 - Determine Bias of Vine Reviews
Using our knowledge of PySpark, we determined if there is any bias towards reviews that were written as part of the Vine program. For this analysis, we determined if having a paid Vine review makes a difference in the percentage of 5-star reviews. Note that many of the datasets for Amazon review categories were missing Vines data, which made the calculating bias statistics impossible for those categories (see Appendix A)
For detailed listings and figures, please refer to Appendix C. In addition, the collected bias stats are shown in Table 2 below.
Answers to the three questions (also shown in Table 2)
-
How many Vine reviews and non-Vine reviews were there?
For the first product category selected for analysis (Furniture), there are 130 Vine and 16,803 non-Vine reviews.
-
How many Vine reviews were 5 stars? How many non-Vine reviews were 5 stars?
For the first product category selected for analysis (Furniture), there are 70 Vine reviews which were 5 stars, and 7,954 non-Vine reviews which were 5 star.
-
What percentage of Vine reviews were 5 stars? What percentage of non-Vine reviews were 5 stars?
For the first product category selected for analysis (Furniture), 53.85% of the Vine reviews were 5 star, and 47.34% of the non-Vine reviews were 5 star.
Table 2 - Final Bias Results for multiple Amazon ‘category’ datasets
| Category | Vines Reviews | Vines 5star | Vines 5star % | Other Reviews | Other 5star | Other 5star% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Books | 4,709 | 1,910 | 40.56% | 101,182 | 46,336 | 45.79% |
| Furniture | 130 | 70 | 53.85% | 16,803 | 7,954 | 47.34% |
| Grocery | 56 | 18 | 32.14% | 26,299 | 14,616 | 55.58% |
| Home Entertainment | 255 | 103 | 40.39% | 22,544 | 10,298 | 45.68% |
| Jewelry | 20 | 10 | 50.00% | 7,064 | 4,075 | 57.69% |
| Musical Instruments | 59 | 34 | 57.65% | 13,452 | 7,674 | 57.05% |
| Software | 231 | 93 | 40.26% | 16,376 | 4,850 | 29.62% |
| Tools | 268 | 149 | 55.60% | 29,452 | 13,668 | 46.41% |
Summary
Is there any bias in Vines reviews?
As shown in Table 2 above, it appears that there is no clear bias for 5-Star ratings in Vines reviews. The complete flow was run on 8 separate Amazon product categories. Simply using the 5-Star ratings for Vines vs. Non-Vines reviews was insufficient. A more thorough analysis would have compared all of the “Star” ratings 1 through 5. In addition, limiting the analysis to reviews with more than 20 votes and helpful percentages over 50% may have been too narrow of a filter to determine bias.
Appendx A - Data Summary and Notes
The Amazon Review Data
The Books dataset was initially chosen for this analysis project. However, the ‘Write review_id_df to RDS’ step took well over two hours and never completed when run on Wed evening. So the process was killed, and a search for a better candidate dataset was done. We downloaded all datasets in order to determine a smaller one, and Video was chosen.
When an attempt to run through the entire flow using the Video dataset, a divide-by-zero exception was encountered while calculating Bias stats in Step 5 of Deliverable 2 because there were no Vines reviews.
At that point all datasets were decompressed, and metrics were collected using awk & perl for each dataset as shown in Table A1 below.
As shown in Table A1, we can see that many of the datasets had no Vine reviews (e.g. Digital_Music_Purchase, Digital_Software, Digital_Video_Download, Digital_Video_Games, Gift_Card, Mobile_Apps, and Video), and the large sizes of some of the datasets seemed to make the process intractable – at least on a weekday. A later run of the Books dataset on an early Saturday morning gave much better runtimes, as shown in Table 1 in the main body of this report. So there is clearly a great deal of variability in the ‘Free Tier’ of Amazon AWS.
Each of the categories in bold font in Table A1 were run through the entire flow. The bias findings are shown in Table 2 in the main body of this report.
Table A1 - Amazon Review Data statistics
| Category | .tsv Rows (millions) | Vine Reviews | .gz file (MBytes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apparel_v1_00 | 5.9 | 2,336 | 619 |
| Automotive_v1_00 | 3.5 | 5,925 | 556 |
| Baby_v1_00 | 1.8 | 12,100 | 341 |
| Beauty_v1_00 | 5.1 | 33,309 | 872 |
| Books_v1_00 | 10.3 | 152,087 | 2,614 |
| Books_v1_01 | 6.1 | 121,395 | 2,568 |
| Camera_v1_00 | 1.8 | 7,883 | 423 |
| Digital_Ebook_Purchase_v1_00 | 12.5 | 32 | 2,566 |
| Digital_Ebook_Purchase_v1_01 | 5.1 | 27 | 1,235 |
| Digital_Music_Purchase_v1_00 | 1.7 | 0 | 242 |
| Digital_Software_v1_00 | 0.1 | 0 | 19 |
| Digital_Video_Download_v1_00 | 4.1 | 0 | 484 |
| Digital_Video_Games_v1_00 | 0.1 | 0 | 27 |
| Electronics_v1_00 | 3.1 | 18,512 | 667 |
| Furniture_v1_00 | 0.8 | 2,775 | 143 |
| Gift_Card_v1_00 | 0.1 | 0 | 12 |
| Grocery_v1_00 | 2.4 | 16,612 | 383 |
| Health_Personal_Care_v1_00 | 5.3 | 32,026 | 965 |
| Home_Entertainment_v1_00 | 0.7 | 2,106 | 185 |
| Home_Improvement_v1_00 | 2.6 | 10,779 | 481 |
| Home_v1_00 | 6.2 | 23,683 | 1,031 |
| Jewelry_v1_00 | 1.8 | 3,815 | 236 |
| Kitchen_v1_00 | 4.9 | 24,434 | 888 |
| Lawn_and_Garden_v1_00 | 2.6 | 13,454 | 465 |
| Luggage_v1_00 | 0.3 | 904 | 58 |
| Major_Appliances_v1_00 | 0.1 | 248 | 24 |
| Mobile_Apps_v1_00 | 5.0 | 0 | 533 |
| Mobile_Electronics_v1_00 | 0.1 | 18 | 22 |
| Music_v1_00 | 4.8 | 1,933 | 1,452 |
| Musical_Instruments_v1_00 | 0.9 | 2,287 | 185 |
| Office_Products_v1_00 | 2.6 | 29,188 | 489 |
| Outdoors_v1_00 | 2.3 | 3,137 | 429 |
| PC_v1_00 | 6.9 | 36,230 | 1,443 |
| Personal_Care_Appliances_v1_00 | 0.1 | 32 | 17 |
| Pet_Products_v1_00 | 2.6 | 10,215 | 492 |
| Shoes_v1_00 | 4.4 | 895 | 613 |
| Software_v1_00 | 0.3 | 10,415 | 90 |
| Sports_v1_00 | 4.9 | 10,080 | 833 |
| Tools_v1_00 | 1.7 | 7,761 | 319 |
| Toys_v1_00 | 4.9 | 41,835 | 800 |
| Video_DVD_v1_00 | 5.1 | 4,340 | 1,443 |
| Video_Games_v1_00 | 1.8 | 4,291 | 454 |
| Video_v1_00 | 0.4 | 0 | 133 |
| Watches_v1_00 | 1.0 | 1,747 | 156 |
| Wireless_v1_00 | 9.0 | 17,481 | 1,626 |
Appendx B - Use Google Colab to read and process data, then write to Amazon RDS
In order to avoid cluttering the main body of this report, all Listings and Figures for Deliverable 1 are shown here in this Appendix B.
Set up PySpark Notebook on Google Colab
Listing B1 - Required Google Colab PySpark startup code
import os
# Find the latest version of spark 2.0 from http://www-us.apache.org/dist/spark/ and enter as the spark version
# For example:
# spark_version = 'spark-3.0.0'
#spark_version = 'spark-3.0.1'
spark_version = 'spark-3.1.2'
os.environ['SPARK_VERSION']=spark_version
# Install Spark and Java
!apt-get update
!apt-get install openjdk-11-jdk-headless -qq > /dev/null
!wget -q http://www-us.apache.org/dist/spark/$SPARK_VERSION/$SPARK_VERSION-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz
!tar xf $SPARK_VERSION-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz
!pip install -q findspark
# Set Environment Variables
import os
os.environ["JAVA_HOME"] = "/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64"
os.environ["SPARK_HOME"] = f"/content/{spark_version}-bin-hadoop2.7"
# Start a SparkSession
import findspark
findspark.init()
Listing B2 - Download the Postgres driver
# Download the Postgres driver that will allow Spark to interact with Postgres.
!wget https://jdbc.postgresql.org/download/postgresql-42.2.16.jar
Listing B3 - Create the SparkSession
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("BigData-Challenge")\
.config("spark.driver.extraClassPath","/content/postgresql-42.2.16.jar")\
.getOrCreate()
Download Data from Amazon AWS into Google Colab PySpark Notebook
Listing B4 - Download the Amazon Review Dataset of interest (Furniture) into ‘df’ dataframe
from pyspark import SparkFiles
url="https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazon-reviews-pds/tsv/amazon_reviews_us_Furniture_v1_00.tsv.gz"
spark.sparkContext.addFile(url)
df = spark.read.option("encoding", "UTF-8")\
.csv(SparkFiles.get(""), sep="\t", header=True, inferSchema=True)
df.show(10)
Figure B1 - Furniture Dataframe read from S3 bucket URL (00:00:00)
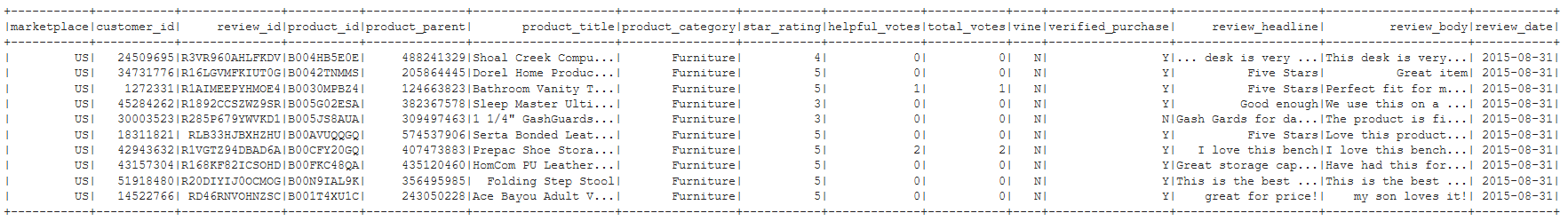
Create Four Tables in RDS database using pgAdmin
Listing B5 - PostgreSQL schema (challenge_schema.sql)
CREATE TABLE review_id_table (
review_id TEXT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
customer_id INTEGER,
product_id TEXT,
product_parent INTEGER,
review_date DATE -- this should be in the formate yyyy-mm-dd
);
-- This table will contain only unique values
CREATE TABLE products_table (
product_id TEXT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL UNIQUE,
product_title TEXT
);
-- Customer table for first data set
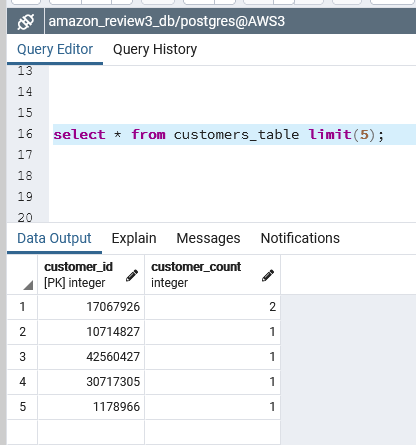
CREATE TABLE customers_table (
customer_id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL UNIQUE,
customer_count INT
);
-- vine table
CREATE TABLE vine_table (
review_id TEXT PRIMARY KEY,
star_rating INTEGER,
helpful_votes INTEGER,
total_votes INTEGER,
vine TEXT,
verified_purchase TEXT
);
Create Dataframes in PySpark for each of the 4 Tables in RDS Database
Listing B6 - Create ‘customers_df’ dataframe from original ‘df’ dataframe
# Create the customers_table DataFrame
# customers_df = df.groupby("").agg({""}).withColumnRenamed("", "customer_count")
from pyspark.sql.functions import count
customers_df = df.groupby("customer_id")\
.agg({"*": "count"})\
.withColumnRenamed("count(1)", "customer_count")
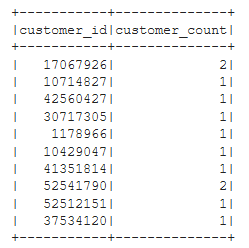
customers_df.show(10)
Figure B2 - customers_df
Listing B7 - Create ‘products_df’ datafrom from original ‘df’ dataframe
# Create the products_table DataFrame and drop duplicates.
products_df = df.select(['product_id', 'product_title']).drop_duplicates()
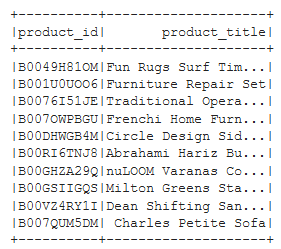
products_df.show(10)
Figure B3 - products_df
Listing B8 - Create ‘review_id_df’ dataframe from original ‘df’ dataframe
from pyspark.sql.functions import to_date
# Create the review_id_table DataFrame.
# Convert the 'review_date' column to a date datatype with
# to_date("review_date", 'yyyy-MM-dd').alias("review_date")
review_id_df = df.select(
[
'review_id',
'customer_id',
'product_id',
'product_parent',
to_date("review_date", 'yyyy-MM-dd').alias("review_date")
]
)
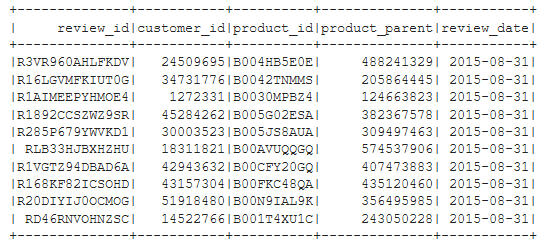
review_id_df.show(10)
Figure B4 - review_id_df
Listing B9 - Create ‘vine_df’ dataframe from original ‘df’ dataframe
# Create the vine_table. DataFrame
vine_df = df.select(['review_id', 'star_rating', 'helpful_votes', 'total_votes', 'vine', 'verified_purchase'])
vine_df.show(10)
Figure B5 - vine_df
Write Dataframes from Google Colab into Amazon RDS Database and Verify
Listing B10 - JDBC setup for database writes
# Configure settings for RDS
from getpass import getpass
password = getpass('Enter database password')
mode = "append"
jdbc_url="jdbc:postgresql://dataviz2.cscg8rwqauuq.us-east-2.rds.amazonaws.com:5432/amazon_review3_db"
config = {"user":"postgres",
"password": password,
"driver":"org.postgresql.Driver"}
Listing B11 - Write ‘review_id_df’ into RDS
# Write review_id_df to table in RDS
# This operation took 2m 10s for 'Furniture' category
review_id_df.write.jdbc(url=jdbc_url, table='review_id_table', mode=mode, properties=config)
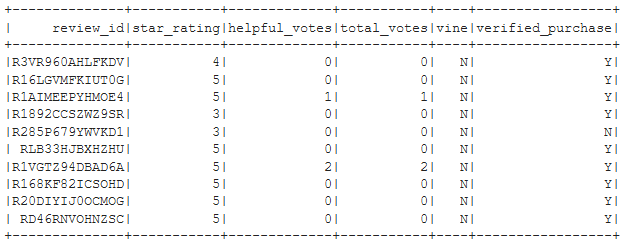
Listing B12 - Verify ‘review_id_table’ table in RDS via pgAdmin on local laptop
select * from review_id_table limit(5);
Figure B6 - First 5 rows of ‘review_id_table’
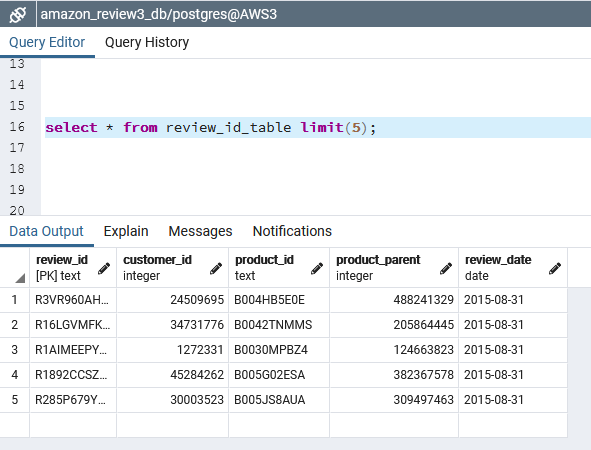
Listing B13 - Write ‘products_df’ into RDS
# Write products_df to table in RDS
# This operation took 1m 15s for 'Furniture' category
products_df.write.jdbc(url=jdbc_url, table='products_table', mode=mode, properties=config)
Listing B14 - Verify ‘products_table’ in RDS via pgAdmin on local laptop
select * from products_table limit(5);
Figure B7 - First 5 rows of ‘products_table’
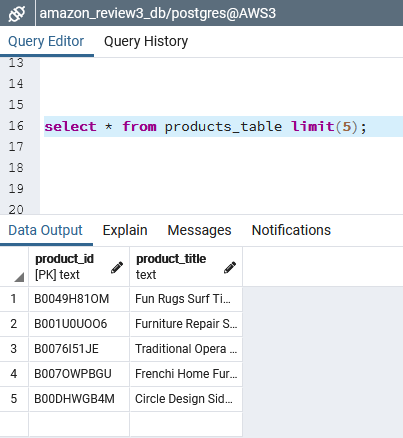
Listing B15 - Write ‘customers_df’ into RDS
# Write customers_df to table in RDS
# Operation took 1m 44s for 'Furniture' category
customers_df.write.jdbc(url=jdbc_url, table='customers_table', mode=mode, properties=config)
Listing B16 - Verify ‘customers_table’ in RDS vis pgAdmin on local laptop
select * from customers_table limit(5);
Figure B8 - First 5 rows of ‘customers_table’
Listing B17 - Write ‘vine_df’ into RDS
# Write vine_df to table in RDS
# Operation took 2m 10s for 'Furniture' category
vine_df.write.jdbc(url=jdbc_url, table='vine_table', mode=mode, properties=config)
Listing B18 - Verify ‘vine_table’ in RDS via pgAdmin on local laptop
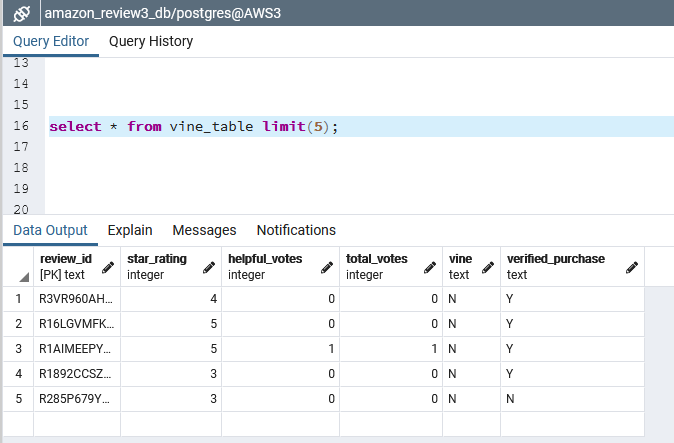
select * from vine_table limit(5);
Figure B9 - First 5 rows of ‘vine_table’
Appendix C - Use Google Colab to read back data from Amazon RDS, and generate bias statistics
In order to avoid cluttering the main body of this report all Listings and Figures for Deliverable 2 are shown here in this Appendix C.
Set up PySpark Notebook on Google Colab
See Listing B1, B2, and B3 above, which are also required for this PySpark Notebook.
Listing C1 - Create the SQLContext in PySpark
from pyspark.sql import SQLContext
sqlContext = SQLContext(spark.sparkContext)
Read back data from Amazon RDS into Google Colab PySpark Notebook
Listing C2 - Read ‘review_id_table’ from RDS to create ‘review_id_df’ dataframe in PySpark
# Read review_id_df from RDS
# Operation took 46s for 'Furniture' category
review_id_df = sqlContext.read.jdbc(url=jdbc_url, table='review_id_table', properties=config)
Listing C3 - Read ‘products_table’ from RDS to create ‘products_df’ dataframe in PySpark
# Read products_df from RDS
# Operation took 9s for 'Furniture' category
products_df = sqlContext.read.jdbc(url=jdbc_url, table='products_table', properties=config)
Listing C4 - Read ‘customers_table’ from RDS to create ‘customers_df’ dataframe in PySpark
# Read customers_df from RDS
# Operation took 11s for 'Furniture' category
customers_df = sqlContext.read.jdbc(url=jdbc_url, table='customers_table', properties=config)
Listing C5 - Read ‘vine_table’ from RDS to create ‘vine_df’ dataframe in PySpark
# Read vine_df from RDS
# Operation took 28s for 'Furniture' category
vine_df = sqlContext.read.jdbc(url=jdbc_url, table='vine_table', properties=config)
Calculate Bias statistics
Listing C6 - Filter ‘vine_df’ to get reviews with more than 20 total votes
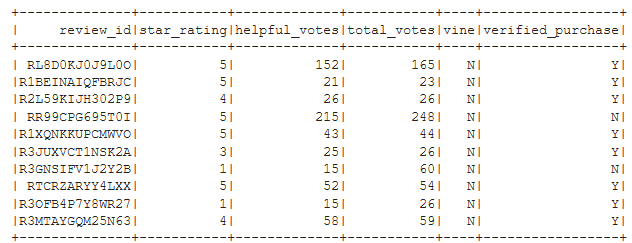
tot_votes_gt_20_df = vine_df.filter("total_votes > 20")
tot_votes_gt_20_df.show(10)
Figure C1 - First 10 rows of ‘tot_votes_gt_20_df’ DataFrame
Listing C7 - Filter ‘tot_votes_gt_20_df’ to get reviews where ‘helpful_votes’ are more than 50% of ‘total_votes’
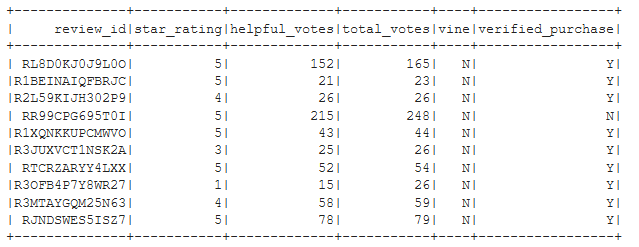
helpful_votes_pct_df = tot_votes_gt_20_df.filter("(helpful_votes / total_votes) > 0.5")
helpful_votes_pct_df.show(10)
Figure C2 - First 10 rows of ‘helpful_votes_pct_df’ DataFrame
 ]
]
Listing C8 - Filter ‘helpful_votes_pct_df’ to get Vine reviews
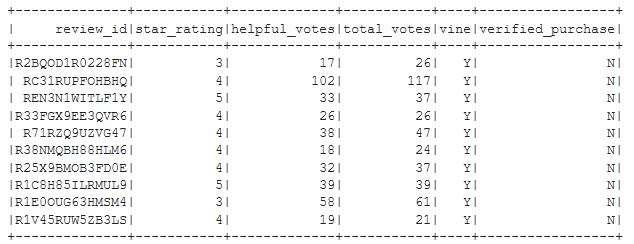
vine_votes_df = helpful_votes_pct_df.filter("vine == 'Y'")
vine_votes_df.show(10)
Figure C3 - First 10 rows of ‘vine_votes_df’
Listing C9 - Same as Listing 26 above, except filter for non-Vine reviews
not_vine_votes_df = vine_df.filter("vine == 'N'")
not_vine_votes_df.show(10)
Figure C4 - First 10 rows of ‘not_vine_votes_df’
Listing C10 - Calculate metrics to determine Vine review bias
n_vines = vine_votes_df.count()
n_other = not_vine_votes_df.count()
n_vine_5stars = vine_votes_df.filter("star_rating == 5").count()
n_other_5stars = not_vine_votes_df.filter("star_rating == 5").count()
pct_vine_5stars = round((n_vine_5stars / n_vines * 100), 2)
pct_other_5stars = round((n_other_5stars / n_other * 100), 2)
print(f"Vines: reviews={n_vines}, 5-star={n_vine_5stars} ({pct_vine_5stars} %)")
print(f"Other: reviews={n_other}, 5-star={n_other_5stars} ({pct_other_5stars} %)")
Figure C5 - Vine review bias statistics of first dataset for ‘Furniture’ category on Amazon

The statistcs n Figure C5 make it look as though there is a bias for 5-Star ratings among Vine Reviews. However, a further analysis of more datasets for other Amazon categories in Table 2 in the main body of this report, shows that Vine vs. Other reviews with 5-Star ratings is all over the map, and there is no clear bias one way or another.